

The Geoid is a reference surface of the Earth and is based on the relationship between gravitational force and gravitational potential that produces a surface where all points are perpendicular to the force of gravity. Geoid-based versus Spheroid/Ellipsoid-based In essence there are 2 types of datums used in Vertical Coordinate Reference Systems: For example misunderstanding the vertical datum can impact planning for a storm surge that may have been measured on a different surface when compared to the height of a constructed LNG plant. I work in the Oil and Gas industry and the application of a correct vertical datum is important in exploration, when defining a height or depth to a geological surface, and also when designing and implementing infrastructure projects such as pipelines, ports and other coastal infrastructure as well as when considering the environmental impacts that spills and other developments may have on coastlines and rivers.
#Vertical datum plus
However in this form MSL is not adequate as a global vertical datum as this mean calculation only exists at the station of measurement and its immediate vicinity, plus the ocean has a dynamic topography that is nicely summarised in this MinutePhysics video. National Ocean Surface, these measurements can be brought together to form a tidal datum. The period of time to measure these variations in the ocean surface was set at 19 years by the U.S. In its simplest form MSL is the average location for the surface of the ocean measured over time to minimise random and periodic variation, such as tides and storm surges.
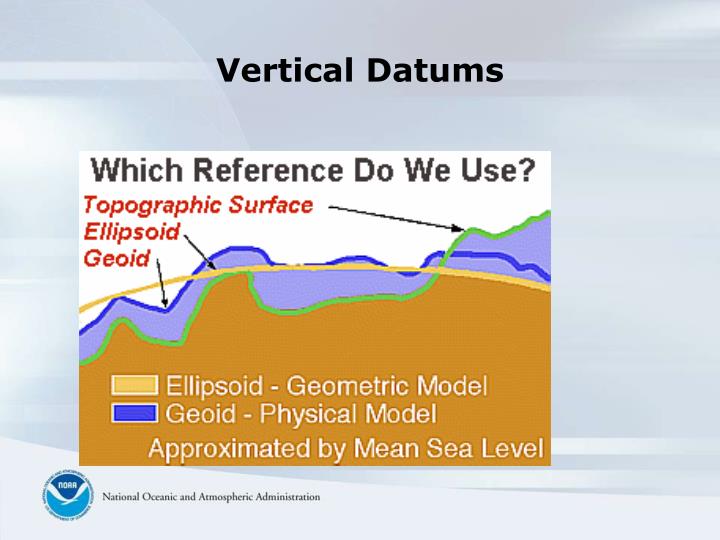
Sea level comes from the Earth' gravity field, therefore gravity is studied to understand height. I n my experience height is colloquially referred to as X units above or below Mean Seal Level ( MSL). Where the gravity field heights are based on the geoid that is defined by a eqipotential surface compared to, for example, the height of a tree using right angle geometry where ground level is defined as 0 height.įigure 1 Difference between the Geoid and Spheroid/Ellipsoid based surfaces and real topography (adapted from ESRI 2012) where h = Ellipsoidal height, N = Orthomatric height and H = Geoid height. It is important to note that the two categories of height are not directly interchangeable as they are completely different. Heights are categorized into two types, those with reference to the Earth's gravity field and those defined on geometry alone.
Geoid (The difference between the ellipsoidal height and the geoid surface Note this can be negative).Orthometric (The difference between the topographic elevation and the geoid).Ellipsoidal (The difference between the topographic elevation and the ellipsoid).T here are various types of height including:

The EPSG dataset currently lists 128 vertical datums worldwide. A datum is required to reach accurate and reliable measures of height above a surface. This reference surface is the Vertical Datum. This definition is concise and direct but leaves a vagueness concerning the reference surface. Is it possible to export in these cases the two heights? This would be useful because if you need to convert those heights to another orthometric system or to ellipsoidal heights in post-processing, having the ellipsoidal height available, it is easier to calculate it.The Geodetic Glossary (2009) defines height as ‘ distance, measured along a perpendicular, between a point and a reference surface’. When using a Vertical Datum different from ellipsoidal heights the program does not save or at least does not export in CSV the ellipsoidal heights, it only exports orthometric heights referred to the shift geoid model. I have a query / request, I have not managed to load a geoid model of my own, for example, in Spain there is the official geoid EGM08_Rednap ( Index of /geoide), this is provided in different formats supported by Topcon, Leica, Trimble, ArcGIS, etc. I am a regular user of reach View 3, I have the app version 7.14.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
